Highlighted Application
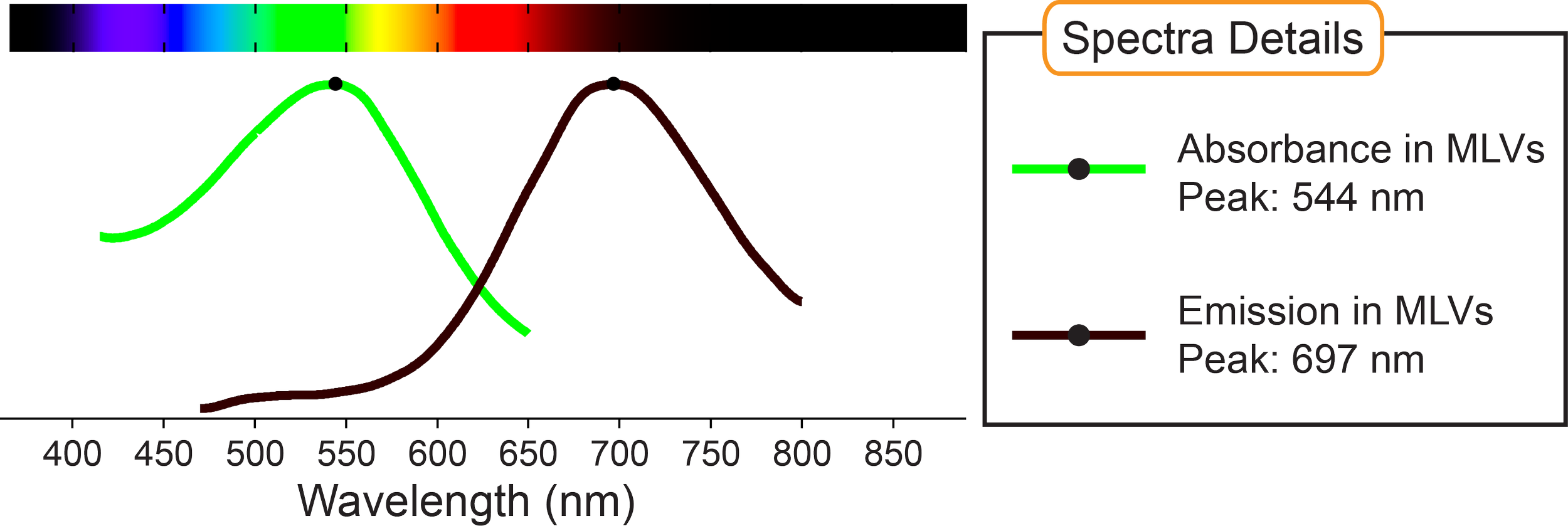
In this video, spontaneously beating human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes stained with ElectroFluor630™ allows ratiometric optical action potential recordings. The ratio of two excitation wavelengths boosts signals and removes artifacts due to non-uniform staining, bleaching, and the motion of these beating (contracting) human heart cells in a dish. Learn more on our Cardiac Research page.
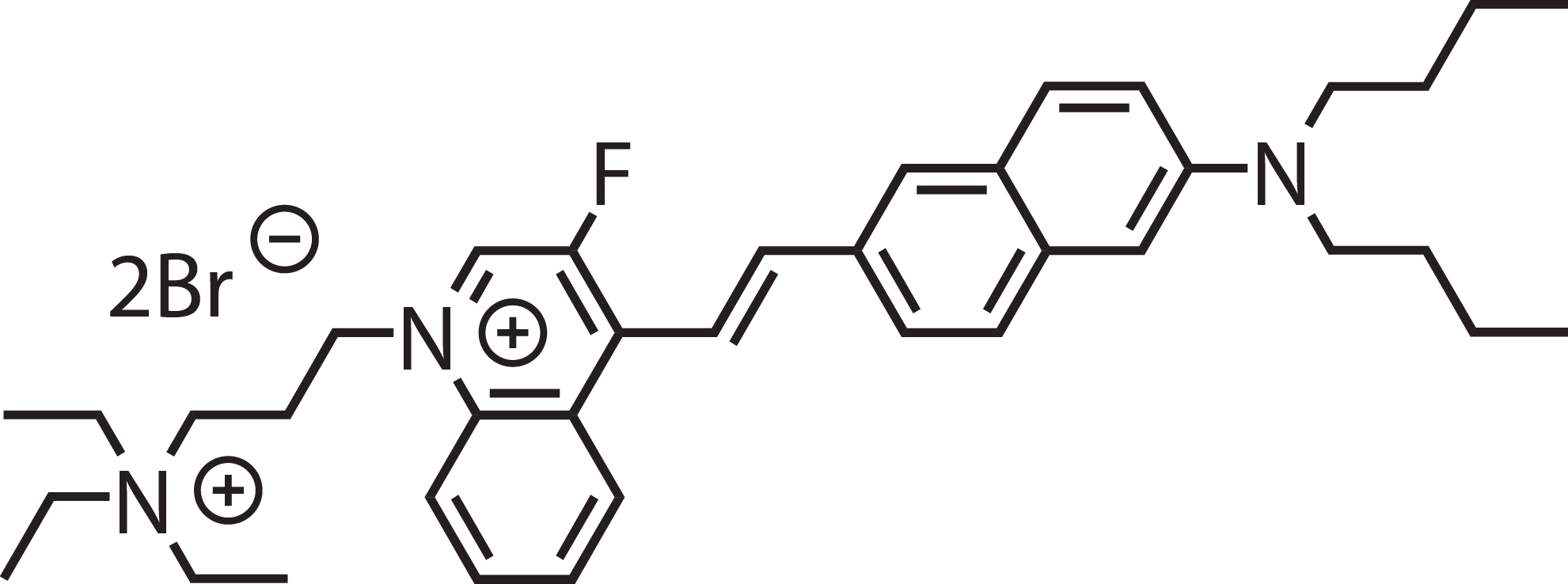
Structure and Spectra
Product Details:
Pre-dried aliquots (solid, solvent removed)
Quantity: 100 nmol / tube (73 μg)
2.0-mL free standing polypropylene tubes
Sealed cap
Individually labeled
References
Lee, P., J. G. Quintanilla, J. M. Alfonso-Almazán, C. Galán-Arriola, P. Yan, J. Sánchez-González, N. Pérez-Castellano, J. Pérez-Villacastín, B. Ibañez, L. M. Loew, and D. Filgueiras-Rama. 2019. In-Vivo Ratiometric Optical Mapping Enables High-Resolution Cardiac Electrophysiology in Pig Models. Cardiovasc Res. PubMed
Yan, P., C. D. Acker, W. L. Zhou, P. Lee, C. Bollensdorff, A. Negrean, J. Lotti, L. Sacconi, S. D. Antic, P. Kohl, H. D. Mansvelder, F. S. Pavone, and L. M. Loew. 2012. Palette of fluorinated voltage-sensitive hemicyanine dyes. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. PubMed