High Throughput Research
Voltage-Sensitive Dyes for High Throughput and Cardiac Toxicology/Safety Screening
High-throughput screening approaches are used by pharmaceutical companies in the drug discovery process to design new pharmaceuticals. Automation allows many compounds to be tested on many plates of cultured cells and imaging approaches (“optical electrophysiology”) with voltage-sensitive dyes lend themselves very well to this parallel screening.
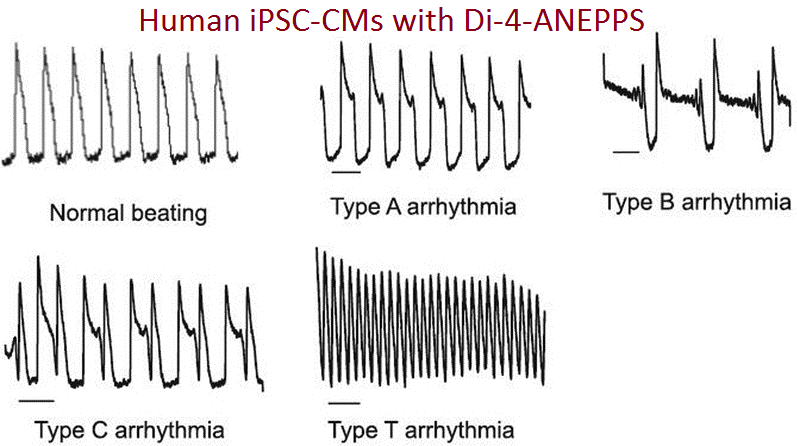
Similar techniques are used for toxicology studies (1-2) for detecting potentially serious cardiac side effects of new drugs. Potentiometric Probes is following the recent developments in cardiac safety screening including the CiPA (Comprehensive In-Vitro Proarrythmia Assay) initiative led by the FDA. Action potential measurements from human stem cell-derived cardiomyocytes are a key component of this initiative and fast voltage-sensitive dyes must be used to capture rapid, transient responses of ion channels upon exposure to developmental drugs and compounds.
Potentiometric Probes is working to tailor existing, fast voltage sensors for this important application, and at the same time, is working on new voltage sensor technology. By advancing 2 separate technologies at the same time, Potentiometric Probes is confident an excellent dye candidate for this application will soon be tested and ready.
Most recently:
- Potentiometric Probes attended the latest CiPA cardiac safety meeting in Washington D.C. in May, 2018 and participated in the cardiomyocyte breakout group.
- Corey Acker attended the latest SPS meeting in Washington D.C. in September/October, 2018.
- Di-4-ANEPPS, was used successfully to carry out CiPA studies in a joint study by the FDA and Clyde Bioscience (2).
- Fluorinated dye Di-4-AN(F)EP(F)PTEA is currently being tested and shows excellent sensitivity in human cardiomyocyte cell cultures.
Citations
- Hortigon-Vinagre, M. P., V. Zamora, F. L. Burton, J. Green, G. A. Gintant, and G. L. Smith. 2016. The Use of Ratiometric Fluorescence Measurements of the Voltage Sensitive Dye Di-4-ANEPPS to Examine Action Potential Characteristics and Drug Effects on Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell-Derived Cardiomyocytes. Toxicol Sci 154(2):320-331. Pubmed
- Blinova, K., J. Stohlman, J. Vicente, D. Chan, L. Johannesen, M. P. Hortigon-Vinagre, V. Zamora, G. Smith, W. J. Crumb, L. Pang, B. Lyn-Cook, J. Ross, M. Brock, S. Chvatal, D. Millard, L. Galeotti, N. Stockbridge, and D. G. Strauss. 2017. Comprehensive Translational Assessment of Human-Induced Pluripotent Stem Cell Derived Cardiomyocytes for Evaluating Drug-Induced Arrhythmias. Toxicol Sci 155(1):234-247. Pubmed
